Secure Your Data with Strong Dynamics GP Backup and Maintenance Strategies
Safeguarding the security and efficiency of your Microsoft Dynamics Great Plains GP database is essential for seamless business operations.
Regular backups and strategic maintenance are key to preventing data loss and ensuring system reliability. Without them, you risk losing critical data and experiencing system performance issues and downtime.
In this blog, we will guide you through the best practices for developing a comprehensive backup strategy and effective maintenance plans for your GP system. We will cover the:
• Importance of backups for your GP database
• Non-SQL files
• Other databases
• Third-party applications
• How often to perform backups and where to store them securely.
• Creating maintenance plans to keep your Dynamics GP system in optimal condition
Why are GP Backups and Maintenance Plans Important?
Dynamics GP backups and maintenance plans are fundamental to the stability and efficiency of your business operations for several compelling reasons, including:
Disaster Recovery
Unexpected events such as ransomware attacks or physical damage can make your server unavailable. A reliable backup ensures you can quickly restore your data and minimize downtime.
Human Error
Mistakes happen, and a robust backup plan allows you to revert to a previous state, mitigating the impact of accidental deletions or changes.
Performance
Regular maintenance keeps your GP system running optimally, preventing performance degradation and ensuring smooth business operations.
Backup Recovery Modes and Types
When setting up database backups, it's crucial to consider both backup recovery modes and backup types. These elements work together to determine how data is backed up and restored effectively. Here’s a breakdown:
Simple Recovery
This involves daily full backups, ensuring that in the event of a failure, only a day's worth of data would be lost. However, to mitigate risks, some also create an additional backup intentionally before significant updates or changes occur. This practice ensures that critical data can be recovered even if an unexpected event interrupts regular backup schedules.
Full Recovery
This includes transaction log backups in addition to full backups, allowing recovery to a specific point in time as long as transaction logs are available. This model offers more granular recovery options, making it ideal for environments where minimal data loss and precise recovery timelines are crucial.
Understanding these modes helps you choose the right strategy based on your data recovery needs and operational priorities.
Including Non-SQL Files in Your Backup Strategy
Non-SQL files encompass various critical components that are integral to daily operations. At Stoneridge Software, we emphasize the importance of including these files in your backup strategy. Here's why each category is essential:
Dynamics GP Share - Software, Other Files
The GP Share is where you organize and store essential software and files crucial for your GP implementation or updates. Including these in your backups ensures that all necessary software and related files are safeguarded against any unforeseen events.
Forms and Reports - Customized Reports and Forms
Custom forms and reports created in Dynamics GP are not stored within the database but as separate files. It's vital to back these customized forms and reports regularly to avoid the risk of losing critical templates and configurations, saving valuable time and effort recreating them.
Custom forms and reports created in Dynamics GP are not stored within the database but as separate files. It's vital to back up these customized forms and reports regularly to avoid the risk of losing critical templates and configurations, saving valuable time and effort in recreating them.
Integrations - Files and Databases
Integrations with GP, such as Integration Manager and Smart Connect, operate on file-based systems. Ensuring backups of both the integration files and associated databases are included in your backup plan guarantees continuity in data integration processes and prevents data loss during system disruptions.
Managing Third Parties and Other Databases
When developing your maintenance plan for GP, it's essential to also consider third-party applications and other databases that are integral to your operations. Here's why they should be included:
Other Databases - Management Reporter, SSRS, and More
Management Reporter and SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS), though not considered third-party, are additional databases used alongside GP. Including these in your maintenance plan ensures comprehensive coverage during backups.
Management Reporter and SSRS do allow reports to be exported, but a good backup plan makes restoration much simpler.
Third Parties - Additional Databases and Files
It is important to identify any other databases associated with third-party applications. Ensuring these databases are part of your maintenance plan guarantees that all critical data sources are backed up regularly. Include any necessary applications or files used daily to ensure they're covered by your recovery options in case restoration is needed.
Incorporating these elements into your maintenance plan enhances resilience and minimizes the risk of data loss, ensuring smooth continuity in your GP operations.
How Often Should You Perform Database Backups?
Determining the frequency of your database backups is important to ensuring data integrity and minimizing potential loss. Here’s a practical approach to help you establish an effective backup routine:
- Full Backups: Perform a full backup once per day - A daily full backup captures the entire database, providing a comprehensive recovery point if needed.
- Log Backups: Execute log backups hourly or more frequently - Regular log backups capture incremental changes and reduce data loss. Depending on your tolerance for data loss, hourly backups are a good standard. Some organizations opt for log backups every five minutes for even greater protection.
- GP Share Backups: Schedule these backups monthly - Monthly backups are usually sufficient for GP Share, considering changes are less frequent. However, if your data changes more often, adjust this to a more frequent schedule.
Forms and Reports Backups: Back up monthly - Like GP Share, forms and reports don’t often change, so a monthly backup is generally adequate. This prevents the need for recreating any custom forms or reports from scratch. - Other Data: Backup frequency depends on data volatility - Assess the nature and criticality of other data types within your system. For database-related data, integrate it into your daily GP maintenance plan. For other files, align with your file backup strategy, typically every month, unless the data changes more frequently.
In short, your backup strategy should align with your organization’s tolerance for data loss and recovery objectives. Daily full backups, frequent log backups, and monthly backups for less frequently changed files form the backbone of a robust GP database maintenance plan.
Where Should You Store Your Backups?
Storing your backups properly is just as important as creating them. Here are some key strategies to ensure your backups are safe and accessible when needed:
- Multiple Local Copies: Store backups on your network in multiple physical locations. This redundancy ensures that if one location is compromised, you still have access to your data.
- Off-Network Storage: Keep some backups off the network, such as in a different building or a remote site. This adds an extra layer of protection against local disasters.
- Cloud Storage: Utilize cloud storage solutions for additional security. While cloud restores might take longer, the data is protected against on-site failures. There are numerous cloud options available, and Stoneridge is happy to help you choose the best one for your needs.
- Regular Testing: Test your backups regularly, at least quarterly, to ensure they are functional. A backup is only useful if it can be successfully restored. Testing helps identify and fix potential issues before they become critical.
A robust backup storage strategy involves multiple local copies, off-network storage, and cloud solutions, combined with regular testing to ensure data integrity and availability.
Maintenance Plans
Implementing comprehensive maintenance plans is essential for ensuring that GP runs optimally. Here’s an overview of the key maintenance tasks you should regularly perform:
Check Database
This task examines the structural integrity of the database and generates a log that needs to be reviewed. Regularly checking the database helps identify and address any issues within the database structure, ensuring its overall health and stability.
Rebuild Index
Rebuilding indexes reduces page splitting and improves data performance. Indexes in GP tables can become fragmented over time, leading to inefficiencies. By regularly rebuilding indexes, you ensure that data can be accessed quickly and efficiently.
Update Statistics
Updating statistics enhances the performance of queries by providing the optimizer with up-to-date information about indexes. This step is crucial for ensuring that queries run smoothly and efficiently, leveraging accurate data for optimal performance.
Setting Up Maintenance Plans in SQL Server
Let’s walk through creating maintenance plans in SQL Server using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). This process ensures that your GP databases are backed up and maintained efficiently. We’ll break it down step-by-step, so even if you're new to SSMS, you'll be able to follow along easily.
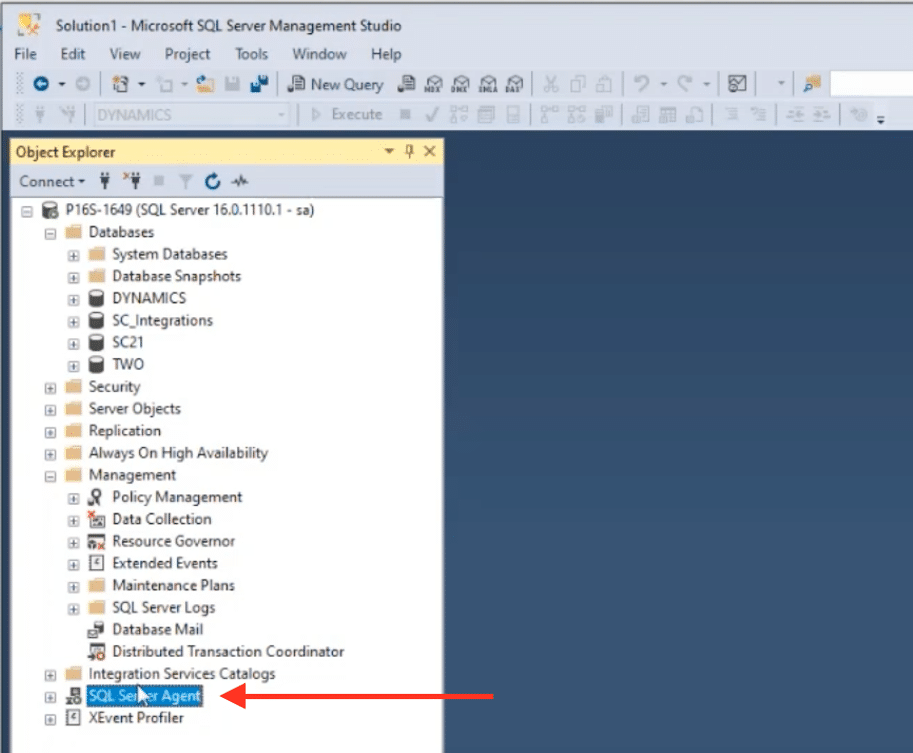
Starting SQL Server Agent
Before we dive into creating maintenance plans, the first step is to ensure that SQL Server Agent is running. This service is crucial as it handles the automation of maintenance tasks. When installing SQL Server, configure SQL Server Agent to start automatically with the server.
Creating a Maintenance Plan
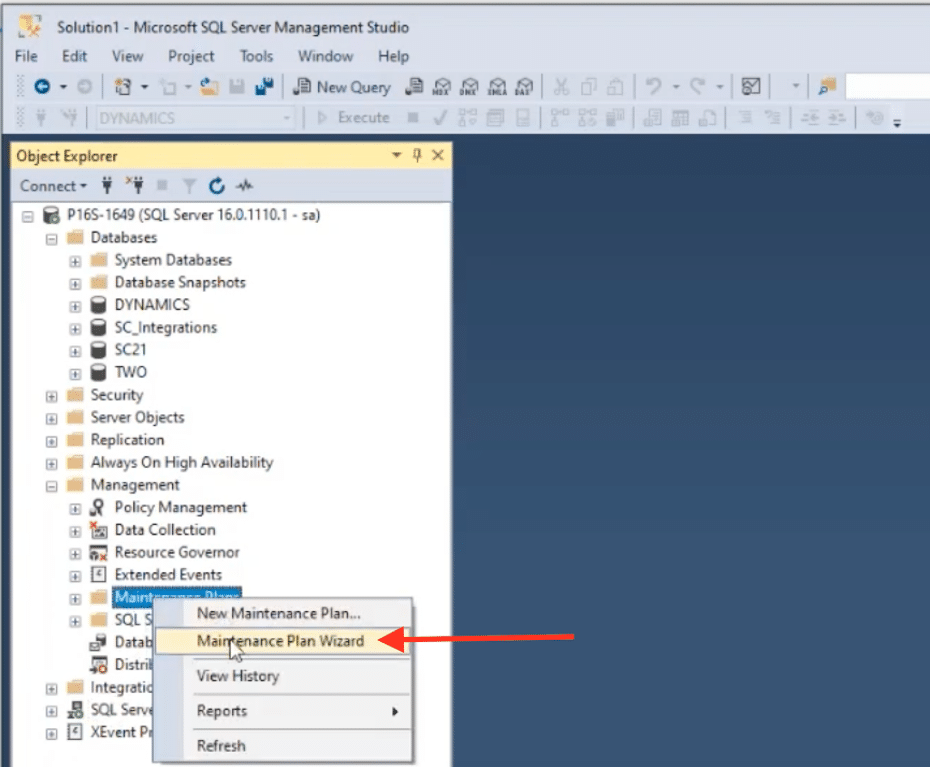
- Open SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS): Launch SSMS and connect to your SQL Server instance.
- Navigate to Maintenance Plans: In the Object Explorer, expand the Management node, then right-click on Maintenance Plans.
- Use the Maintenance Plan Wizard: It's always a good idea to use the wizard if available. Click on the Maintenance Plan Wizard to start the process.
Scheduling the Maintenance Plan
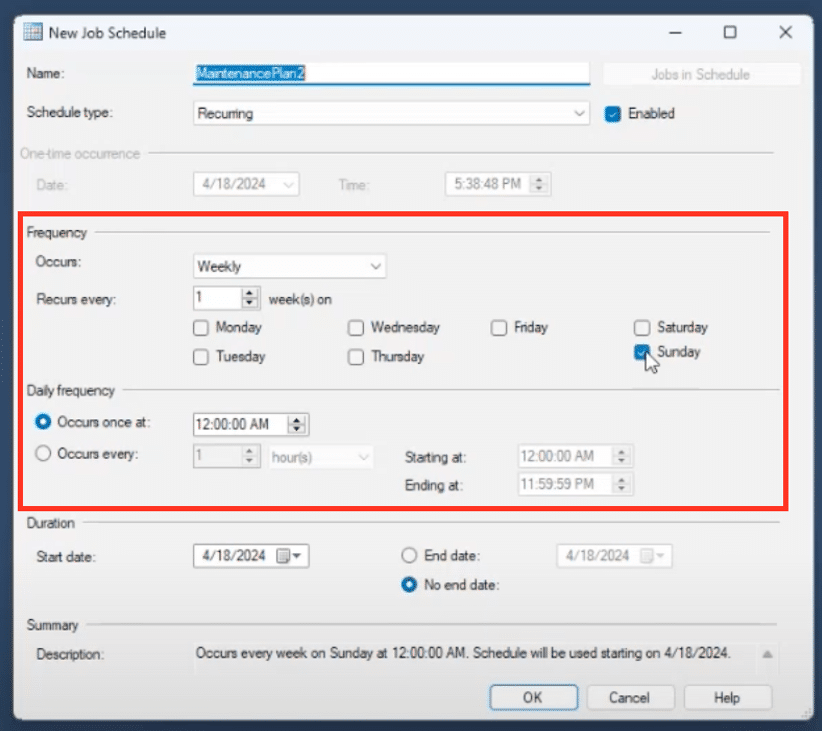
1. Set Up a Schedule
The wizard will prompt you to create a schedule for the maintenance plan. It's advisable to run maintenance tasks during off-peak hours, such as late at night or on weekends. For example, you might schedule it for Saturday or Sunday night, or early in the morning on weekdays.
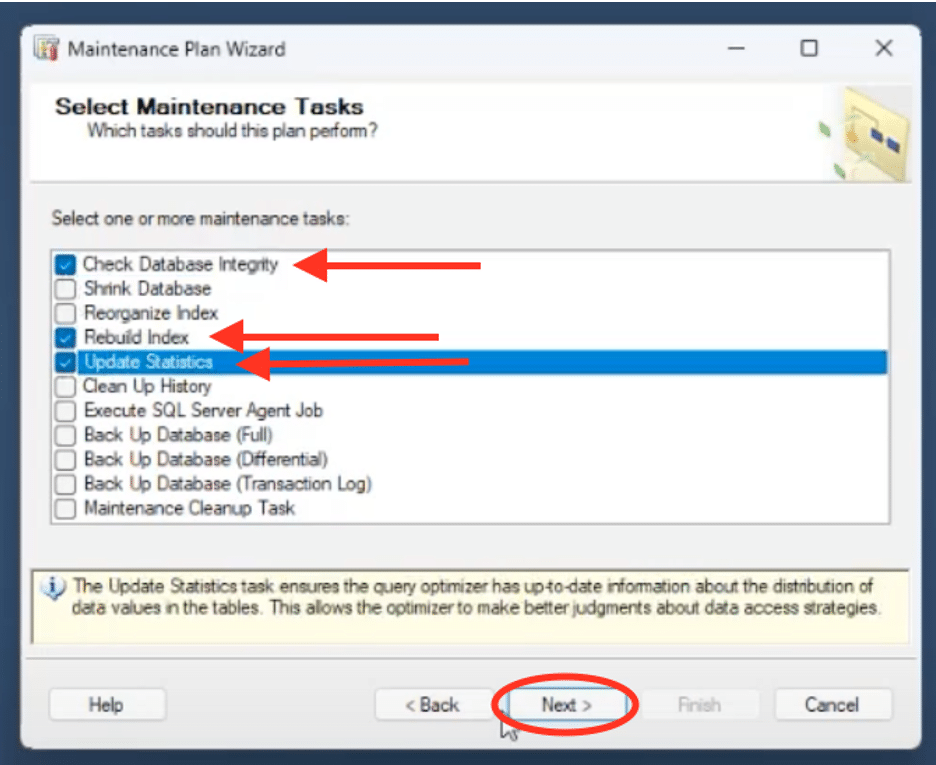
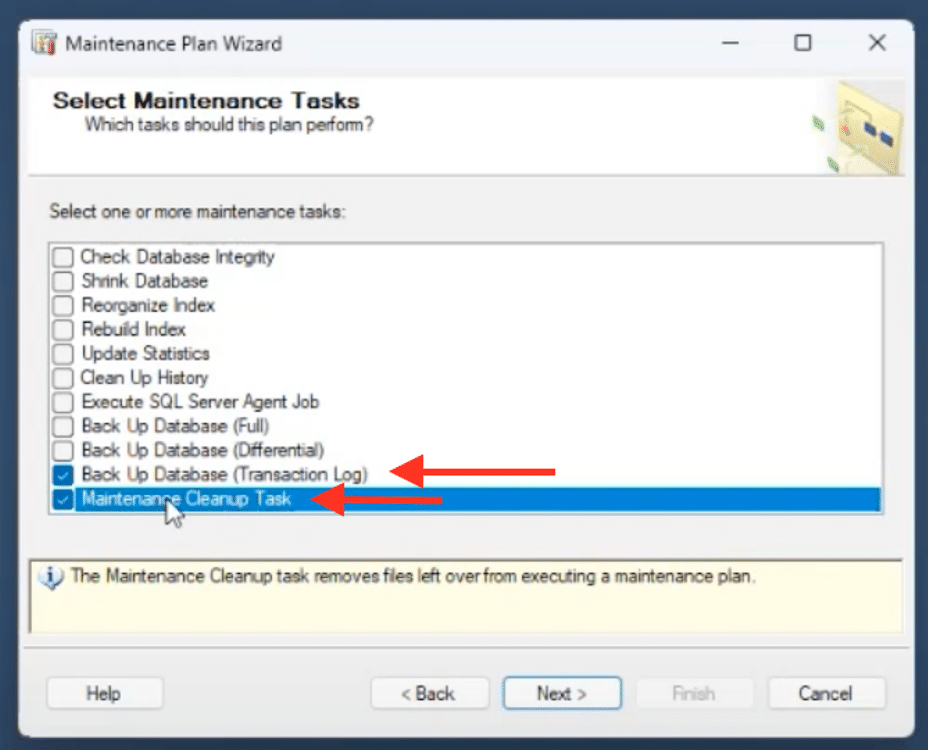
2. Select Maintenance Tasks
Choose the maintenance tasks recommended by Microsoft:
- Check Database Integrity
- Rebuild Index
- Update Statistics
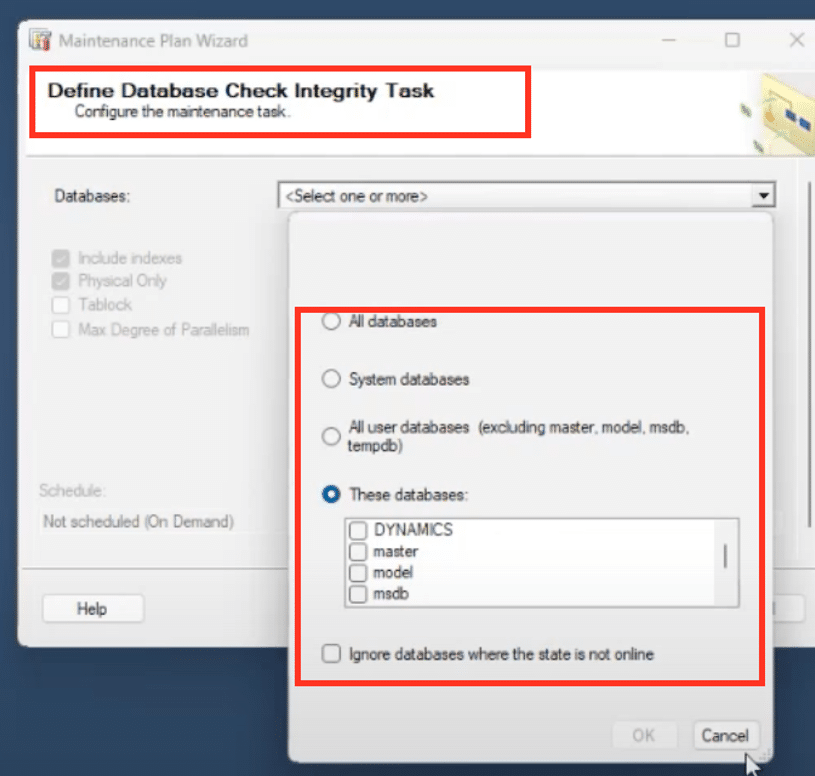
3. Select Databases
Generally, you'll want to apply these tasks to all user databases. Specifically, select databases like Dynamics, Management Reporter, Report Server, and any company databases related to GP.
Configuring Database Backups
1. Full Backups
It's a good practice to create separate maintenance plans for different types of backups. For full backups, create a plan that runs daily. In the selection screen, choose the full backup task and include a maintenance cleanup task to delete old backups after a certain number of days. Aim to retain at least seven days' worth of backups, provided your storage allows for it.
2. Transaction Log Backups
Similarly, set up a separate maintenance plan for transaction log backups. Include a maintenance cleanup task for these as well. While it might seem like overkill, separating these tasks can help manage them more effectively.
Finalizing the Maintenance Plan
Once you've configured the tasks and schedules, review your settings to ensure everything is correct. Save and apply the maintenance plan. Regularly monitor the plan to ensure it's running as expected and adjust the schedule or tasks based on your system's performance and requirements.
This overarching structured approach ensures your GP databases are well-maintained, minimizing the risk of data loss and optimizing system performance. With these steps, you can set up and manage your SQL Server maintenance plans effectively.
Want to Learn More About Protecting Your Data in Dynamics GP?
Get in touch with Stoneridge Software! Our Dynamics GP team can help you establish strong backup and maintenance strategies to help you achieve optimal performance.
Under the terms of this license, you are authorized to share and redistribute the content across various mediums, subject to adherence to the specified conditions: you must provide proper attribution to Stoneridge as the original creator in a manner that does not imply their endorsement of your use, the material is to be utilized solely for non-commercial purposes, and alterations, modifications, or derivative works based on the original material are strictly prohibited.
Responsibility rests with the licensee to ensure that their use of the material does not violate any other rights.