Scheduled Payments in Dynamics GP
Scheduled payments in Microsoft Dynamics GP is a great tool to use if you need to pay off an invoice over time such as setting up a payables invoice with a set payment schedule over five payments. This tool is not a largely used piece of GP but can be quite useful.
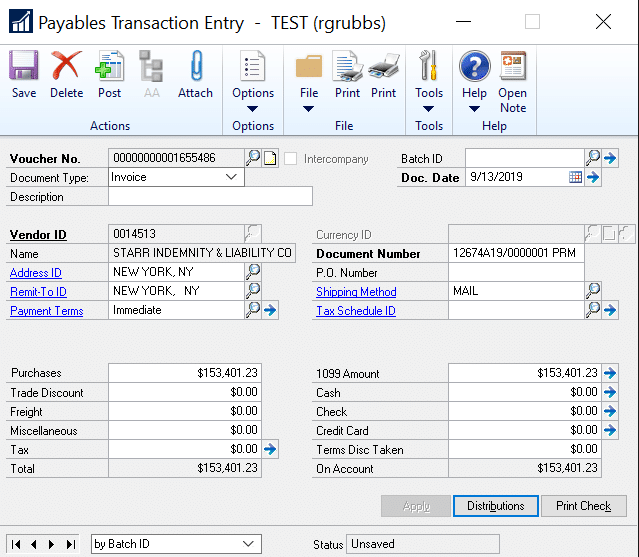
Enter Payables Invoice
Purchasing > Transactions > Transaction Entry
Create the Payment Schedule
Purchasing > Transactions > Scheduled Payments
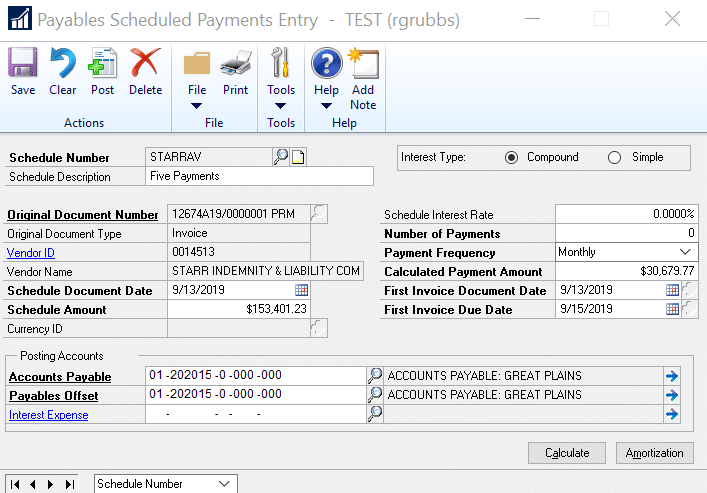
- When you open the scheduled payments window a default schedule number will appear, you can modify it if you want
- Enter a schedule description
- Select the original document number (this is the payables invoice you created)
- The schedule document date displays the date of the original document used to create this payment schedule
- The scheduled amount is amount of the original invoice, you can modify this if you only want to pay a portion of the invoice through scheduled payment. This amount will be used when calculating the amortization schedule
- In your example, the original invoice is for $154,401.23, with payments due in five equal monthly installments.
- The schedule amount is the amount that will go into the payables offset account
- Enter the scheduled interest rate and whether the interest if compound or simple (not applicable for this example).
- Compound – Calculate interest on the initial principal and any accumulated unpaid interest
- Simple – Calculate interest only on the initial principal
- Enter the number of payments that this schedule will be divided into. This number is used when calculating the amortization schedule
- Select the frequency of the payments for this schedule: semimonthly, monthly, quarterly, semiannual, or annual
- Click CALCULATE on the bottom right of the window and the system will calculate the Calculated Payment Amount which displays the payment amount that is calculated when the amortization schedule is created
- Enter the First Invoice Document Date which is the invoice date for the first scheduled payment invoice
- Enter the First Invoice Due Date which is the due date for the first scheduled payment invoice
- Enter the posting accounts:
- Accounts Payable – Enter or select the account to be credited with the total schedule amount, not including interest, when the payment schedule is posted. The account will be debited with the scheduled payment amount, including principal and interest, when an individual payment is posted using the Post Payables Scheduled Payments window
- Payables Offset – Enter or select the account to be debited with the total schedule amount, not including interest, when the payment schedule is posted. The account will be credited with the scheduled payment amount, not including interest, when an individual payment is posted using the Post Payables Scheduled Payments window
- Interest Expense – Enter or select the account to be credited with the interest portion of the scheduled payment amount when an individual payment is posted using the Post Payables Scheduled Payments window. This account is not debited when you post a payment schedule.
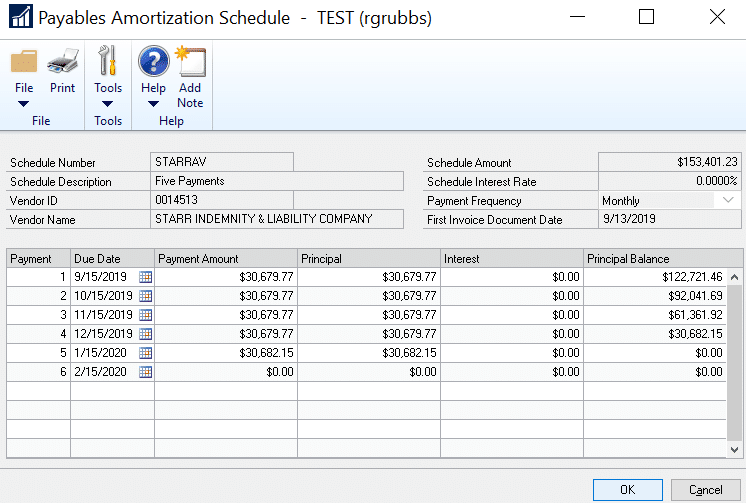
Amortization Schedule
Purchasing > Transactions > Scheduled Payments > click Amortization
If there is no interest, you can edit the due date and the payment amount for each line in the scrolling window.
- To edit the due date, you can either enter the date manually (MM/DD/YYYY) or click the calendar to select a date
- To modify the payment amount simply click the field and enter the new amount
- Note: the total of all the lines must equal the schedule amount on the top right of the window otherwise you will receive an error message
Under the terms of this license, you are authorized to share and redistribute the content across various mediums, subject to adherence to the specified conditions: you must provide proper attribution to Stoneridge as the original creator in a manner that does not imply their endorsement of your use, the material is to be utilized solely for non-commercial purposes, and alterations, modifications, or derivative works based on the original material are strictly prohibited.
Responsibility rests with the licensee to ensure that their use of the material does not violate any other rights.