Find Customer Data Fast with Copilot’s Natural Language Search in Dynamics 365
One of the most underreported, yet biggest, issues in business applications is the simple task of finding information.
Even with clean data and intuitive views, users often struggle to navigate between different screens, lists, filters, field names, column configurations, and advanced query builders. As organizations collect more data than ever before, that struggle will only grow.
Enter Microsoft Copilot Natural Language Search: Find Data Fast!
Natural language search capabilities in Copilot can solve this problem by making data discovery as simple as typing a sentence in your own words. This feature is a huge step forward in how you can navigate your Dynamics 365 environments. It is also hugely helpful for users who aren’t technical, new employees who don’t know the schema behind the scenes or simply want a faster way to find data relevant to their jobs.
In this blog, we will:
- Define Copilot Natural Language Search and how it will benefit your organization
- Walk through how it works
- Show you how to enable or disable the feature inside your environment.
What Is Copilot Natural Language Search?
At its core, Copilot Natural Language Search brings an intuitive, conversational search layer to Dynamics 365 views and grids. Instead of clicking through filters, dropdowns, and configuration options, users can type what they want in everyday language, and Copilot interprets it into the correct query. In other words, instead of constructing formal filters or sorting rules, users can simply describe the data they want.
While the questions or prompts your team uses will vary based on your unique business needs, here are some examples:
- “Show me open opportunities.”*
- “What is the current open rate and click rate for our monthly newsletter?”*
- “Summarize recent emails, Teams meetings, and phone calls with [client name] in the past six months and provide me with highlights.”*
- “How much downtime have we reported for production in the past year?”*
- “What is our customer satisfaction score based on the results of our recent customer survey?”*
- Note: These are example prompts. The types of prompts you can use with Copilot Natural Language Search will depend on how your system is customized and if it is storing the applicable data.
Why This Feature Matters
For many organizations, data access is an ongoing challenge, and there are many drawbacks to not using natural language search, including:
- Users often memorize a handful of views and avoid building new ones: While trusting the views you are familiar with is good, it can hinder efficiency gains and make your system complacent.
- Filters are intimidating for those who aren’t technical: Not everyone who needs to access data will have a full understanding of what it means, which can make filtering a challenge.
- Teams waste time clicking through advanced search options: This takes up extra time and sometimes leaves users disappointed if they can’t find a search option that fits their needs.
- IT and admin staff often end up creating views for people: This takes their focus away from their primary role in protecting your data and environment.
- Important insights can go unnoticed because users don’t know how to surface them: Human error happens, and people might overlook a key piece of data and omit it from a data search.
How Copilot Natural Language Search Helps Users
Copilot natural language search addresses these issues head-on by:
- Reducing training needs: Instead of teaching users how to apply filters or navigate query builders, they just type what they need.
- Improving productivity: Finding information becomes instantaneous—helpful for teams working quickly in sales, service, operations, and management contexts.
- Bridging the technical knowledge gap: Users no longer need to know field names, schema names, or structured filter syntax.
- Encouraging broader use of data: When it’s easy to search, people search more often and make more informed decisions.
Simply put, it saves you time and frees up team members from across your organization to focus on the tasks that are most relevant to them.
Copilot Natural Language Search in Action
Now let’s walk through how Copilot Natural Language Search behaves inside Dynamics 365 to give you a clear sense of how users interact with it day-to-day.
Starting with an Accounts View
When you open a view—such as All Accounts—you’ll notice something new. Instead of the classic search bar with “begins with” filters, you now see a banner at the top with the Copilot icon. This indicates that natural language search is available.
From here, users can type their query directly into the Copilot search bar.
Example 1: Finding Accounts Missing a Main Phone Number
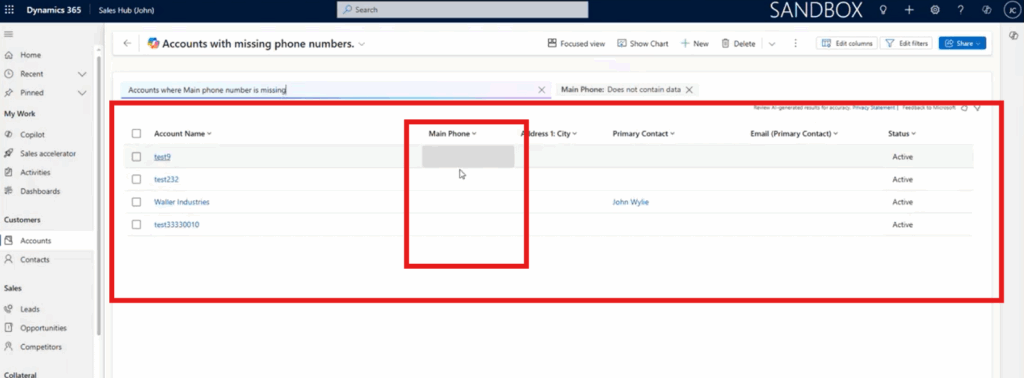
In what is a common scenario, a sales or admin team wants to find accounts with incomplete contact information so they can talk to those clients and update their files. To find this, they can avoid technical jargon and simply type: “Accounts where the main phone number is missing.”
Copilot will correctly interpret the request and add a filter for “Main phone – does not contain data." Copilot was able to translate the intent and apply filters to find the information. This saves the user from having to go through additional steps like:
- Finding and knowing the field name
- Selecting a filter, such as “does not contain data”
- Managing complicated menus
Example 2: Adding More Filters Through Natural Language
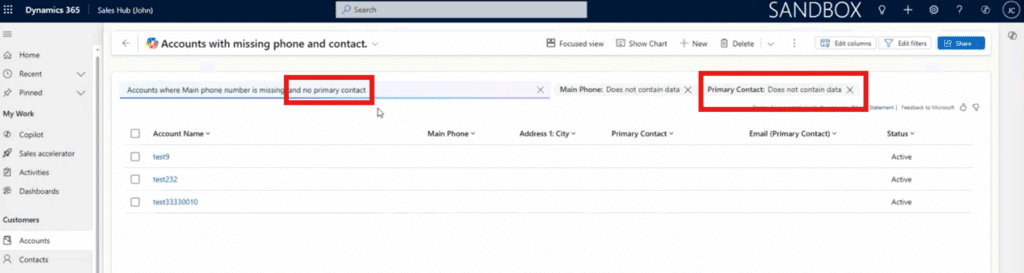
Say this same user wants to add another filter. They can simply use a second prompt or update the existing one. In this case, they might add “and no primary contact.” Copilot will then add another filter called “Primary contact – does not contain data.”
From there, you should have a tidy list of the data you are looking for. You can also click on Edit Filters to verify the logic.
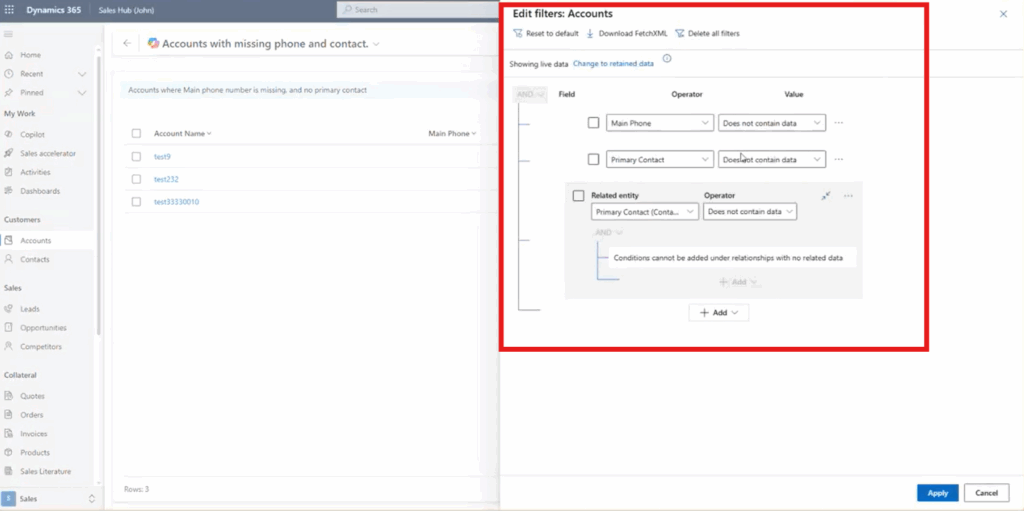
Managing Filters Manually
Even when using Copilot, you keep full control over your search and can verify results. Clicking on Edit Filters lets you verify the logic Copilot uses and can see the filters applied directly in your view.
You can also edit or remove filters with a single click or toggle conditions without retyping anything. This ensures you maintain control over your data.
Simply put, natural language doesn’t completely replace traditional filtering, but it significantly enhances it.
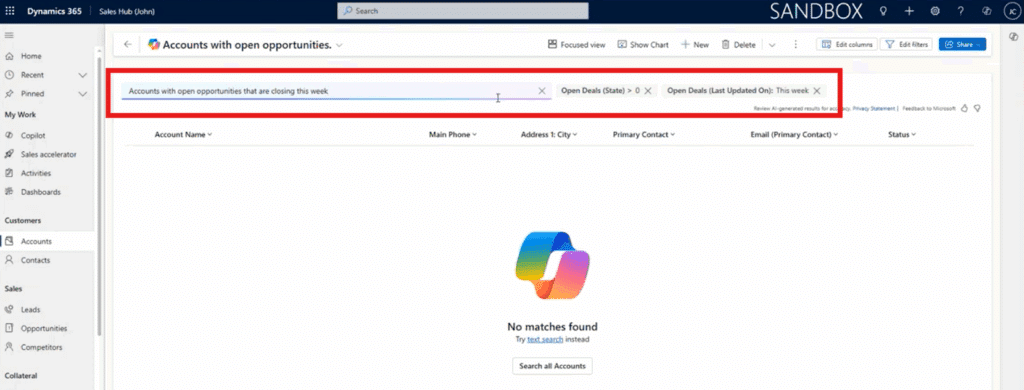
Example 3: Searching Opportunities Closing This Week
Imagine you are a sales rep and want to summarize your opportunities, so you are prepared to go into next week. You can use Copilot chat in the Opportunities view to type: “Opportunities closing this week.”
Copilot will recognize the user intent, the correct field (Estimated Close Date), and the correct dynamic filter for “this week.” Copilot automatically applies the right logic, which is powerful because the user did not need to specify:
- “Estimated Close Date”
- The exact field or table name
- Whether the filter should be dynamic or fixed
- Any specific date range
Dynamic Dates vs. Fixed Dates
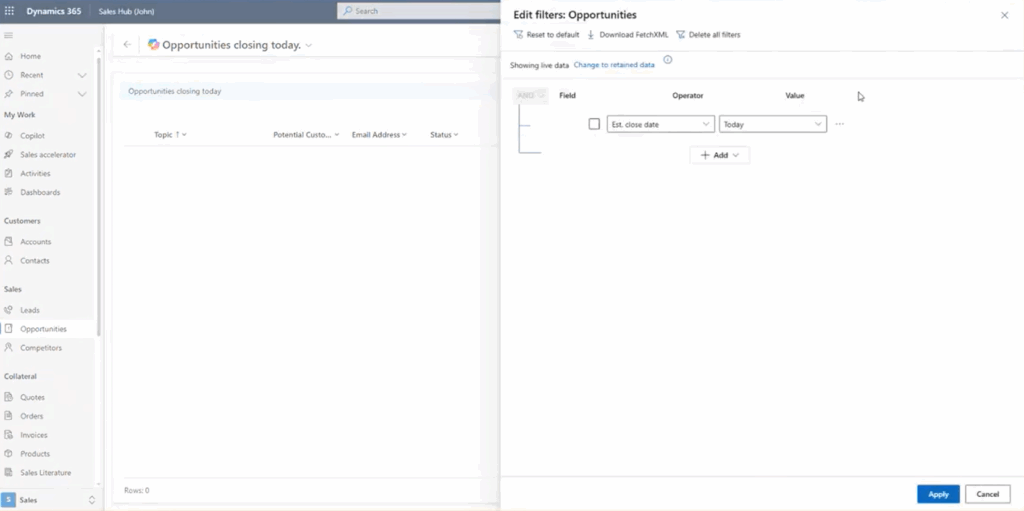
Copilot can also choose dynamic date filters as opposed to fixed date filters. This helps streamline your prompts as you won’t have to rewrite them for a different day of the month.
For example, if a sales rep asks Copilot for “opportunities closing today,” this could be interpreted as:
- Estimated Close Date = Today (dynamic), or
- Estimated Close Date is 2025-12-15 (fixed date example)
Copilot correctly chooses the dynamic version, ensuring the view remains useful in the future. So if that same sales rep decides to do the same thing a week later, Copilot will pick up on the fact that they want to see opportunities closing on the day they type the prompts.
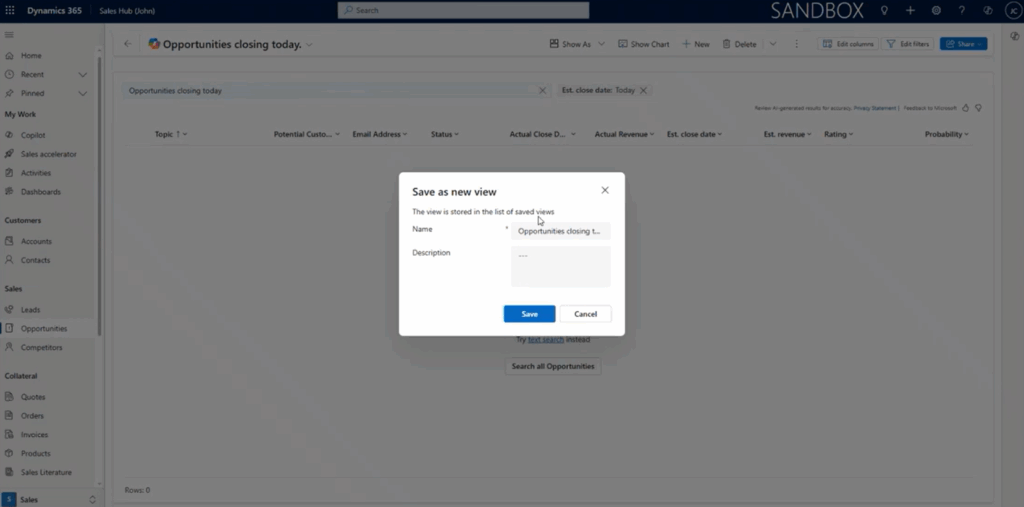
Saving Copilot-Generated Views
If a user wants to keep the results, they can save them as a new view—just like any custom view. You can edit, add, and remove columns, and make it your own. Dynamics even adds a Copilot icon next to the view name, so users know it was created via natural language search. This enables your team to leverage automation without requiring manual intervention.
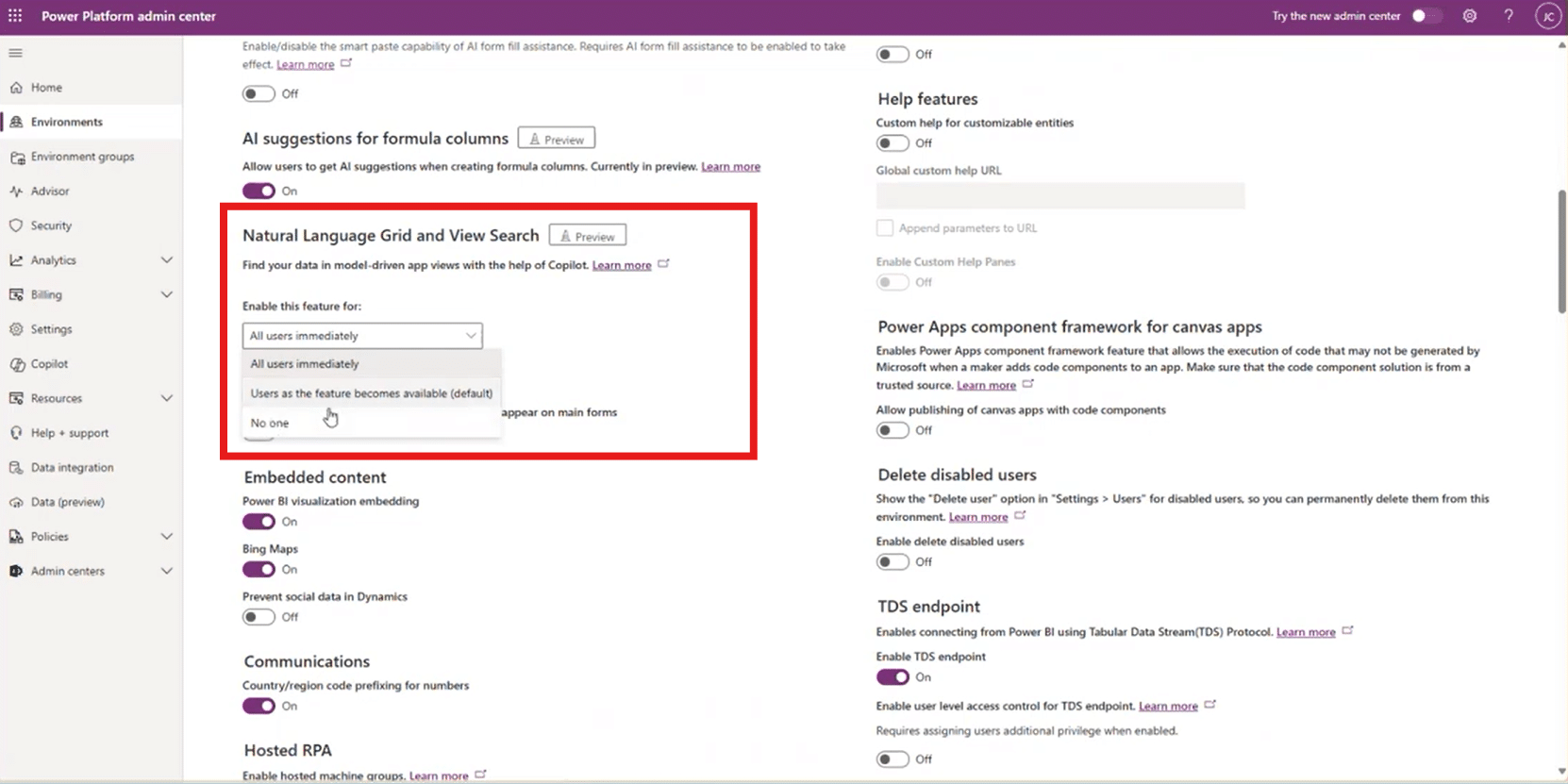
How to Enable or Disable Copilot Natural Language Search
Organizations vary widely in how they want users to interact with data. Some clients love natural language search immediately; others prefer their teams to continue using structured, traditional views. The good news is that enabling or disabling the feature is easy by simply following these steps:
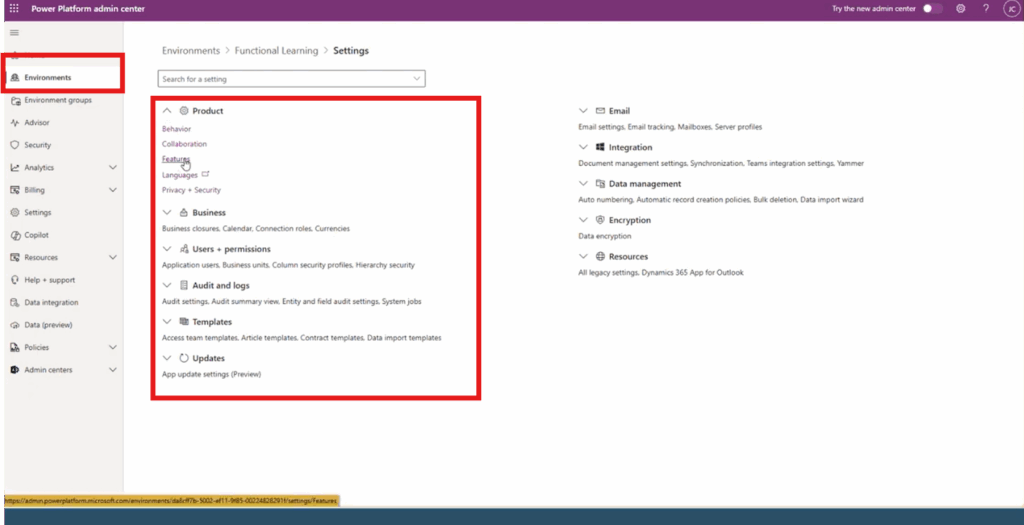
- Go to the Power Platform Admin Center: Navigate to the environment where you want to modify settings.
- Open the Environment Settings: Select your environment, then click Settings.
- Open Product > Features: A list of product-level capabilities will appear.
- Locate Copilot Features: On the left panel, you’ll see several AI and Copilot configuration options.
- Find “Natural Language Grid and View Search”: This feature is included in a long list of Copilot features on this page.
- Use the drop-down menu to choose your preference:
- All Users: Enables the feature for everyone as soon as it becomes available to your environment.
- Users as the feature becomes available: If the feature is in preview, this option will automatically enable the feature once it’s publicly available.
- No One: Disables it completely. Copilot search will not appear, regardless of availability.
This toggle gives organizations full control over rollout timing, user exposure, and training needs. Your team and organization are unique, and Microsoft gives you the flexibility to tailor your natural language search function to what you need.
Why an Organization Might Disable It (Temporarily)
But wait! If Copilot Natural language search is great, why would you want to disable it?
The easy answer is that it depends on the organization. While natural language search is a great way to find data fast without having to dig through views or tables, some clients may want to disable the feature because:
- Users may not understand what to type
- Teams may prefer a more structured data access approach
- IT may want the feature to mature before rolling it out
- Organizations with strict data governance sometimes prefer only predefined views
At the end of the day, the feature can be turned on or off to fit your organizational needs.
Talk to the Stoneridge Experts Today to Get Started!
Copilot Natural Language Search is one of the clearest examples of AI’s value inside business applications. It transforms a traditionally technical and time-consuming task into something conversational, intuitive, and fast.
Stoneridge experts will help you set this feature up in your environment and analyze your systems to find areas where it can help you the most.
Reach out to our team today to get started.
Under the terms of this license, you are authorized to share and redistribute the content across various mediums, subject to adherence to the specified conditions: you must provide proper attribution to Stoneridge as the original creator in a manner that does not imply their endorsement of your use, the material is to be utilized solely for non-commercial purposes, and alterations, modifications, or derivative works based on the original material are strictly prohibited.
Responsibility rests with the licensee to ensure that their use of the material does not violate any other rights.